Bio-plastic from coffee grounds: technical properties, applications and advantages

The environmental toll of traditional plastics has fueled interest in bio-based alternatives that not only reduce dependency on fossil fuels but also mitigate waste. Coffeefrom® has entered this niche by developing thermoplastic materials in which the recycled coffee grounds constitute a new input, offering distinct technical and mechanical advantages across various applications.
Table of Contents
Composition of bioplastic with coffee
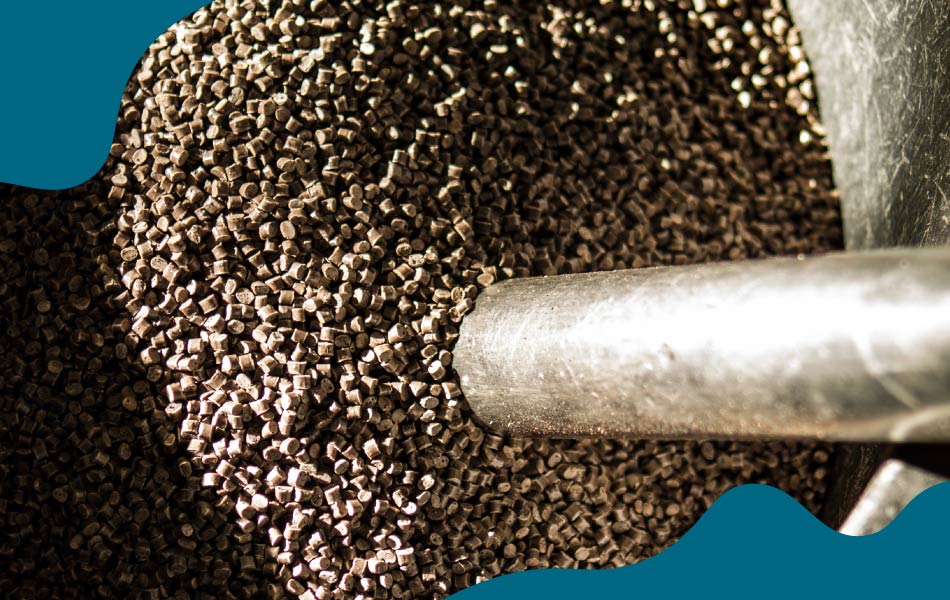
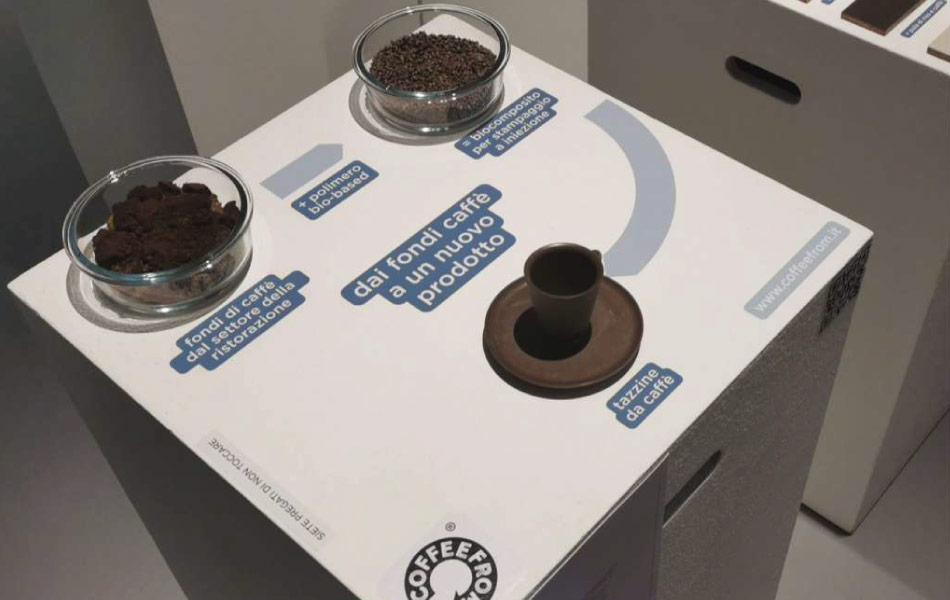
At Coffeefrom® we integrate coffee grounds into our formulations, creating three primary materials:
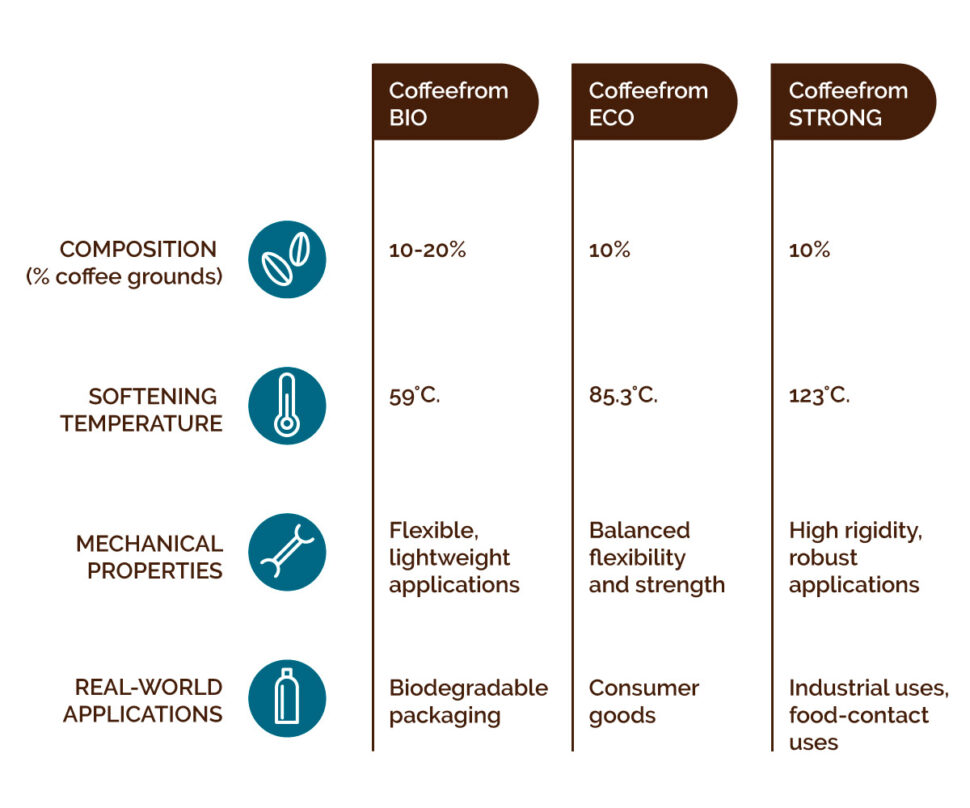
- Coffeefrom® Bio: composed of 10-20% coffee grounds and PLA (polylactic acid), a biodegradable biopolymer, this material is designed for applications that require flexibility and light weight.
- Coffeefrom® Eco: contains 10% coffee grounds mixed with recycled low-density polyethylene (LDPE), balancing flexibility with strength.
- Coffeefrom® Strong: features 10% coffee grounds combined with high-density polyethylene (HDPE), providing high rigidity and thermal resistance.
The inclusion of coffee grounds not only enhances the sustainability profile of these materials but also imparts unique aesthetic and functional properties. The granular texture and natural color variations from coffee grounds contribute to a distinctive look, while also reinforcing the material structure. This synergy between coffee content and plastic polymers ensures that these materials can effectively replace conventional plastics in a range of applications.

Thermal properties of coffee-based plastic
Thermal properties are crucial in determining the suitability of materials for various applications. The melt temperature (Tm) and softening temperature are specific characteristics of thermoplastic materials that indicate their behavior under heat.
- Coffeefrom® Bio: with a softening temperature of 59°C, it is suitable for applications requiring moderate thermal stability, such as certain consumer goods, packaging, automotive, tableware and service products.
- Coffeefrom® Eco: boasts a softening temperature of 85.3°C, making it suitable for uses that demand a balance between flexibility and thermal endurance, such as flexible packaging and some industrial components.
- Coffeefrom® Strong: its high softening temperature of 123°C allows it to perform well in environments requiring high rigidity and thermal resistance, like automotive parts and heavy-duty containers.
Compared to conventional plastics, these coffee-based plastics offer competitive thermal performance while reducing environmental impact. For instance, HDPE, a common fossil-based plastic, has a softening temperature in the range of 120-140°C, which aligns closely with Coffeefrom® Strong. This makes coffee-based plastics a viable alternative for many applications traditionally dominated by conventional polymers.
Mechanical strength – Young’s modulus
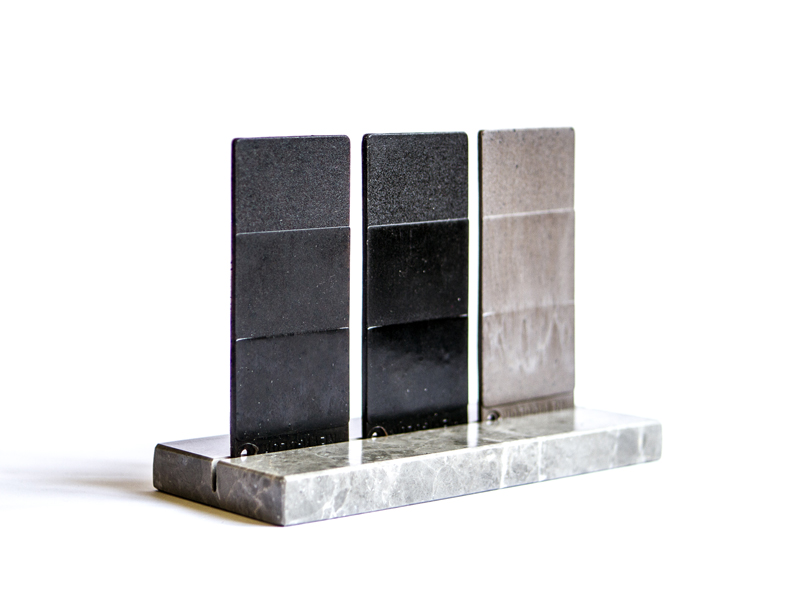
Young’s Modulus is a measure of a material’s stiffness and is indicative of its ability to withstand deformation under stress. The mechanical properties of Coffeefrom® materials are tailored to suit different applications:
- Coffeefrom® Bio: this material is designed for flexibility and lightweight applications, making it ideal for items like flexible packaging, disposable utensils, and lightweight consumer goods. Its lower Young’s Modulus reflects its pliability and resilience under varying loads.
- Coffeefrom® Eco: offers a balanced profile of flexibility and strength, suitable for a wide range of applications that require durability without compromising on flexibility. Examples include flexible industrial components and semi-rigid containers.
- Coffeefrom® Strong: exhibits high rigidity and robustness, comparable to conventional high-density plastics. This makes it perfect for demanding applications where structural integrity is critical, such as automotive parts, high-stress packaging, and industrial equipment.
The mechanical performance of these materials ensures they can replace traditional plastics in diverse settings, contributing to reduced plastic waste and a lower carbon footprint.

Real-world applications and performance benefits
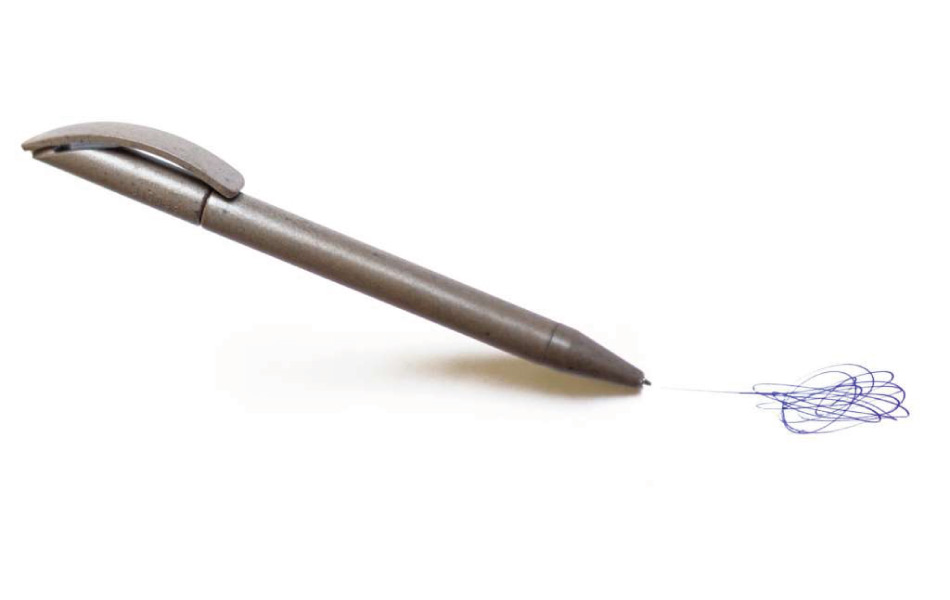
The practical applications of coffee-based thermoplastic materials are vast, spanning from everyday consumer products to specialized industrial uses. Some notable applications include:
- Packaging: Coffeefrom® Bio is excellent for creating biodegradable packaging that reduces plastic waste while offering the flexibility needed for various packaging formats.
- Consumer goods: Coffeefrom® Eco is well-suited for products like reusable containers, personal care items, and flexible packaging solutions that require a balance of strength and flexibility.
- Industrial uses: Coffeefrom® Strong’s high rigidity and thermal resistance make it ideal for applications such as automotive components, durable containers, and industrial parts that demand robust performance. Having also received the food contact approval, it can be used as a primary material for food keepers, snack wrappers and more. *
In addition to functional benefits, coffee-based materials provide significant sustainability and economic advantages. By repurposing coffee grounds—a byproduct of the coffee industry—these materials contribute to a circular economy, reducing waste and promoting resource efficiency. Furthermore, the biodegradability of Coffeefrom® Bio and potential for lower greenhouse gas emissions during production make them attractive options for companies looking to enhance their environmental credentials.

Conclusion
Coffee-based thermoplastic materials offer a compelling blend of technical advantages and sustainability benefits. Their tailored properties make them suitable for a wide range of applications, from flexible consumer goods to rigid industrial components. This not only supports environmental sustainability but also opens up new avenues for integrating waste materials into valuable products, demonstrating the future potential of bio-based materials in a sustainable economy.
Coffeefrom®’s pioneering approach exemplifies how creative reuse of natural byproducts can lead to sustainable, high-performance materials that meet the diverse needs of modern industries. As the world moves towards more sustainable practices, the role of such innovative solutions will be crucial in shaping a greener future.