The use of bioplastics in food packaging

As sustainability becomes increasingly important, the food packaging industry is under pressure to reduce its reliance on fossil-fuel-derived plastics. Bioplastics, made from renewable biological sources or designed to be biodegradable, are emerging as a viable alternative. The adoption of bioplastic in food packaging is driven by regulatory changes, consumer demand, and the need to lessen environmental impact. Understanding the key types of bioplastics, their benefits, and their role in the market is crucial for stakeholders in the food packaging sector.
Table of Contents
Types of bioplastics in food packaging
In the food packaging industry, several bioplastics stand out for their practical applications and performance:
- Polylactic acid (PLA):
PLA is derived from fermented plant starches like corn or sugarcane. It’s widely used due to its availability and cost-effectiveness.
PLA is ideal for disposable items such as cups, clamshells, and trays, offering clarity and rigidity. However, PLA has limitations in heat resistance and flexibility, making it less suitable for hot food applications unless modified.
- Polyethylene aerephthalate (Bio-PET):
Bio-PET is partially made from renewable resources like sugarcane. It shares similar properties to traditional PET but has a reduced carbon footprint.
Bio-PET is used for beverage bottles and packaging films due to its durability and excellent barrier properties against gases and moisture, which help extend the shelf life of food products. Bio-PET retains the transparency, strength, and recyclability of conventional PET, making it versatile for various packaging needs.
- Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA):
PHAs are produced by microbial fermentation of organic substrates such as sugars. They are fully biodegradable and decompose in different environments, including marine conditions.
PHAs are used in flexible packaging like films and bags, as well as in rigid items like bottles. Despite their good barrier properties and flexibility, PHAs are generally more expensive to produce, which can limit their use in cost-sensitive applications.

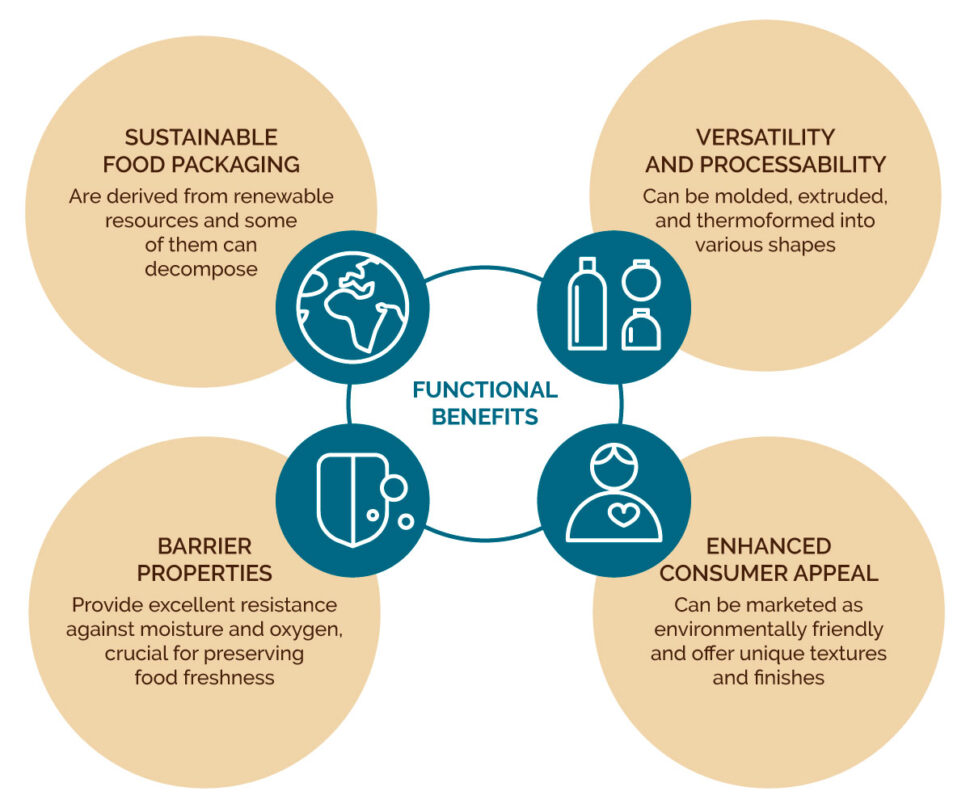
Functional benefits for food packaging
Bioplastics offer several functional benefits that make them appealing for food packaging applications:
- Sustainable food packaging
Many bioplastics are derived from renewable resources, reducing dependence on fossil fuels and lowering the carbon footprint.
Bioplastics like PLA and PHA can decompose under industrial composting conditions, reducing waste in areas where recycling is not feasible,
- Barrier Properties:
Bioplastics such as PLA and Bio-PET provide excellent resistance against moisture and oxygen, crucial for preserving food freshness and extending shelf life.
- Versatility and processability:
Bioplastics can be molded, extruded, and thermoformed into various shapes, from rigid containers to flexible films, making them suitable for a wide range of packaging applications. Many bioplastics can be processed using conventional plastic manufacturing equipment, facilitating their adoption without significant changes to production lines.
- Enhanced consumer appeal:
Packaging made from bioplastics can be marketed as environmentally friendly, appealing to consumers who prioritize sustainability. This eco-friendly branding can enhance brand reputation and attract eco-conscious customers. Bioplastics can offer unique textures and finishes that differentiate products on shelves, adding to their visual appeal and marketability.
Environmental impact
Bioplastics present several environmental advantages over traditional plastics:
- Reduction in Carbon Footprint:
Bioplastics like PLA and Bio-PET, derived from renewable sources, have a lower carbon footprint compared to fossil-fuel-based plastics, aiding in overall environmental impact reduction.
Certain bioplastics, such as PLA and PHA, are designed to biodegrade under specific conditions, which helps in reducing the environmental burden of plastic waste.
Compostable bioplastics can break down into non-toxic components in industrial composting facilities, offering a valuable waste management solution, especially for food packaging contaminated with organic residues.
- Reduction in plastic pollution:
Some bioplastics, notably PHA, can degrade in marine environments, providing potential solutions to ocean plastic pollution. This is particularly relevant for single-use plastics that are prone to ending up in waterways.
- Resource efficiency:
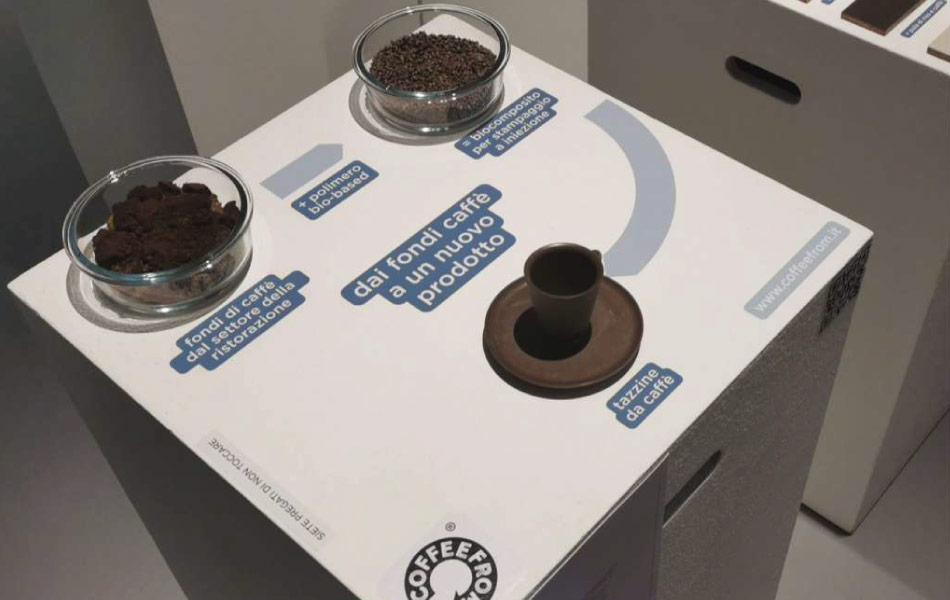
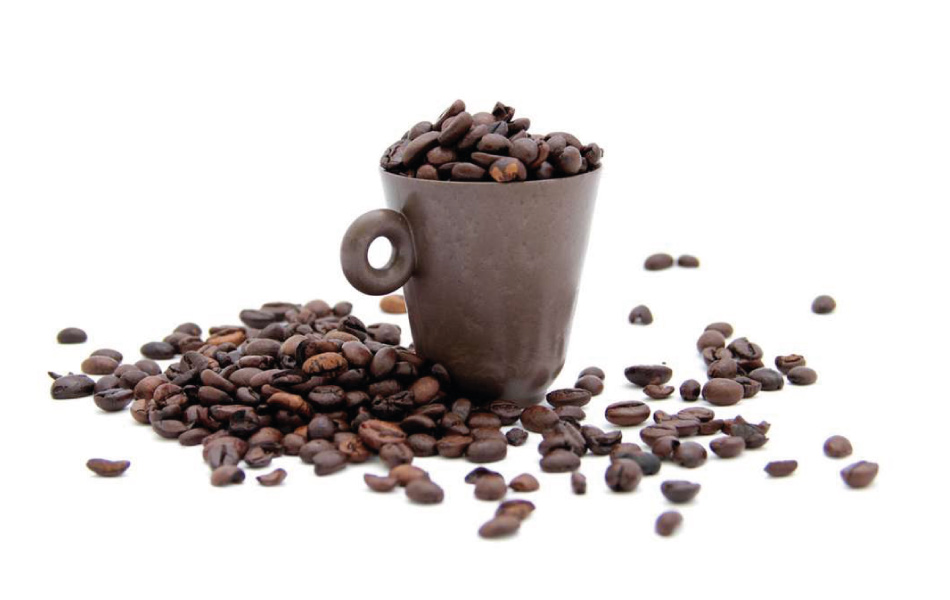
Using renewable feedstocks for bioplastics promotes efficient resource use. Innovations in feedstock sourcing, such as using agricultural by-products or non-food crops (eg. spent coffee grounds), enhance the sustainability of bioplastic production.
Economic and market trends
The market for bioplastics in food packaging is rapidly expanding due to a confluence of consumer demand, regulatory pressure, and technological innovation.
As consumers become more environmentally conscious, they prefer food products with sustainable packaging, prompting brands to adopt bioplastic packaging to enhance their competitive edge.
New regulatory initiatives are aiming at reducing plastic waste and promoting renewable materials, including bans on single-use plastics and incentives for sustainable packaging options. The establishment of standards and certifications for compostability, biodegradability, and bio-based content is building market trust and clarity around bioplastics.
Innovations are improving the performance of bioplastics, making them more competitive with traditional plastics by enhancing their barrier properties, strength, and heat resistance. As production scales up and efficiencies increase, the cost of bioplastics is decreasing, making them more accessible.
Significant investments in research and development are leading to the discovery of new materials and enhancements in existing ones. Collaboration between bioplastic producers, packaging manufacturers, and brands is essential for developing and adopting bioplastic solutions, which are crucial for scaling their market presence and ensuring the long-term sustainability of the packaging industry.
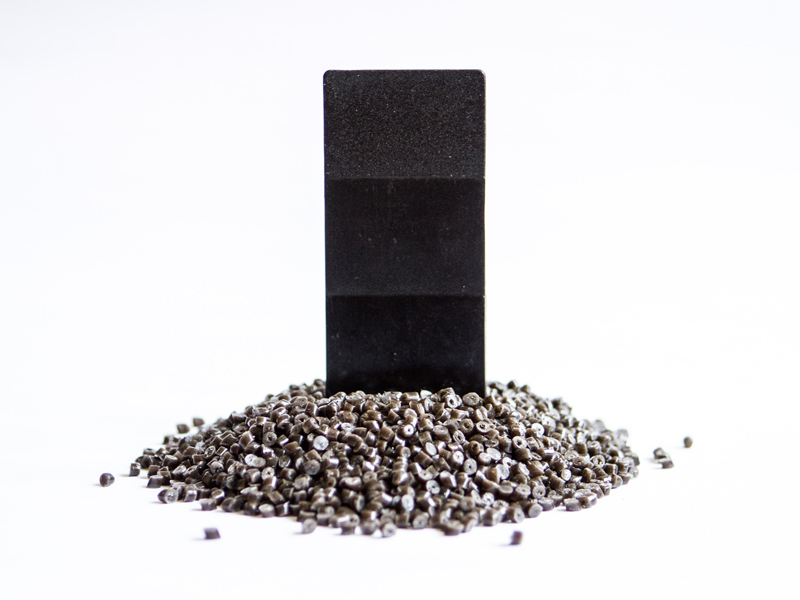

Coffefrom Strong: HDPE and coffee grounds
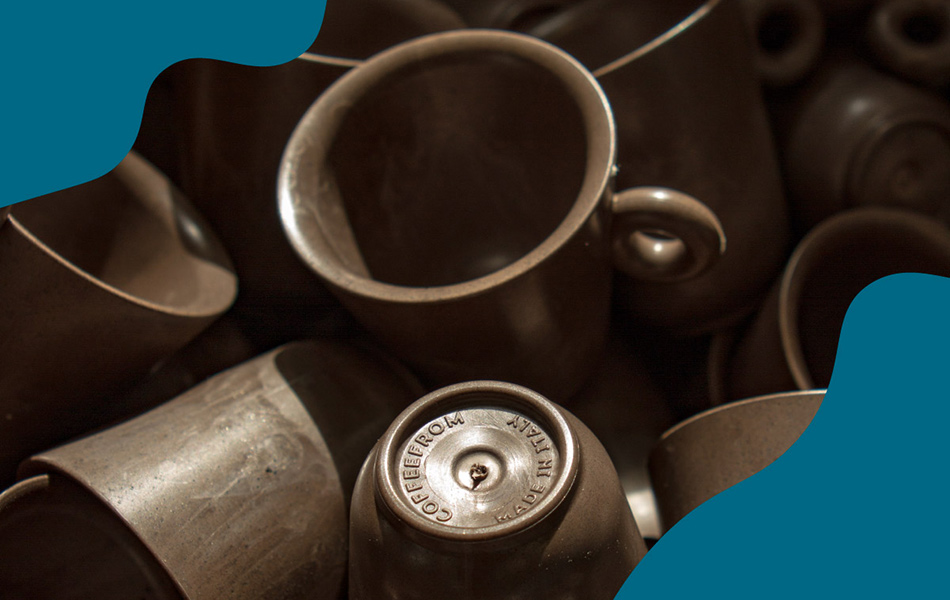
Our Coffefrom strong material, which blends coffee grounds of industrial origin (10%) mixed with high density polyethylene (HDPE), has recently been approved for food contact. Although not a proper bioplastic because of the presence of fossil HDPE, its coffee content enhances its sustainability and promotes circular economy in an industry characterized by high volume of waste. The potential application of the material are multiple, such as easter eggs plastic jars, compostable wrappers for snack bars and freshness-preserving food containers
CTA: Find out more about Coffee from strong
Conclusion
Bioplastics offer the food packaging industry a pathway to meet sustainability goals and evolving consumer expectations. As technology advances and production costs decrease, their adoption is likely to grow, providing viable alternatives to traditional plastics that meet the functional demands of packaging.
By adopting bioplastics, companies can reduce their environmental impact, enhance their brand image, and contribute to global efforts to mitigate plastic pollution and reduce carbon emissions. The food packaging sector is at the forefront of this transformation, with bioplastics poised to play a crucial role in shaping its sustainable future.
Finally, while bioplastics offer significant environmental benefits, managing their full lifecycle impacts, from production to disposal, is crucial for maximizing their advantages.ble practices, the role of such innovative solutions will be crucial in shaping a greener future.