Spent coffee grounds: transforming waste into wealth

In the quest for sustainability, the reuse of agricultural byproducts has emerged as a key strategy. Among these, spent coffee grounds stand out due to their vast availability and untapped potential. With coffee being one of the most consumed beverages globally, the byproduct generated— coffee grounds—offers numerous opportunities for reuse across various industries. This blog delves into the significance of repurposing spent coffee grounds, exploring their potential applications and the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead.
Table of Contents
Scope of coffee waste
Globally, coffee consumption is staggering, with over 3 billion cups consumed daily. This immense consumption leads to significant waste, with approximately 7-8 million tons of spent coffee grounds produced annually (Circular economy in the coffee sector). Often discarded in landfills, these grounds contribute to greenhouse gas emissions and environmental degradation. Thus, rethinking their disposal is crucial to minimizing environmental impact and enhancing resource efficiency.
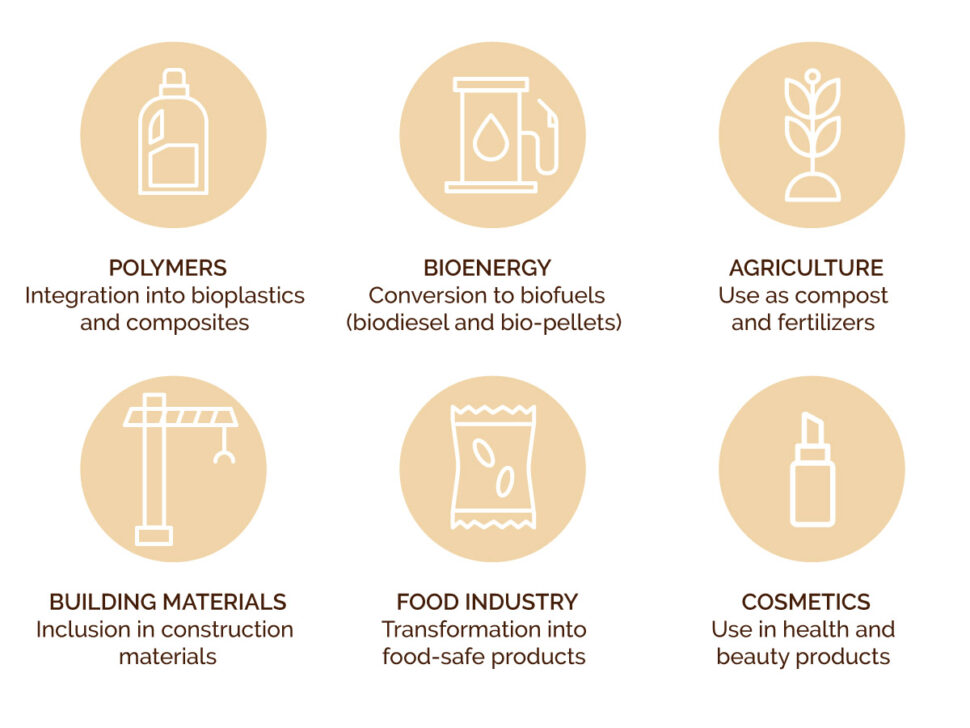
Industrial applications of spent coffee grounds
Polymers: integration into bioplastics and composites
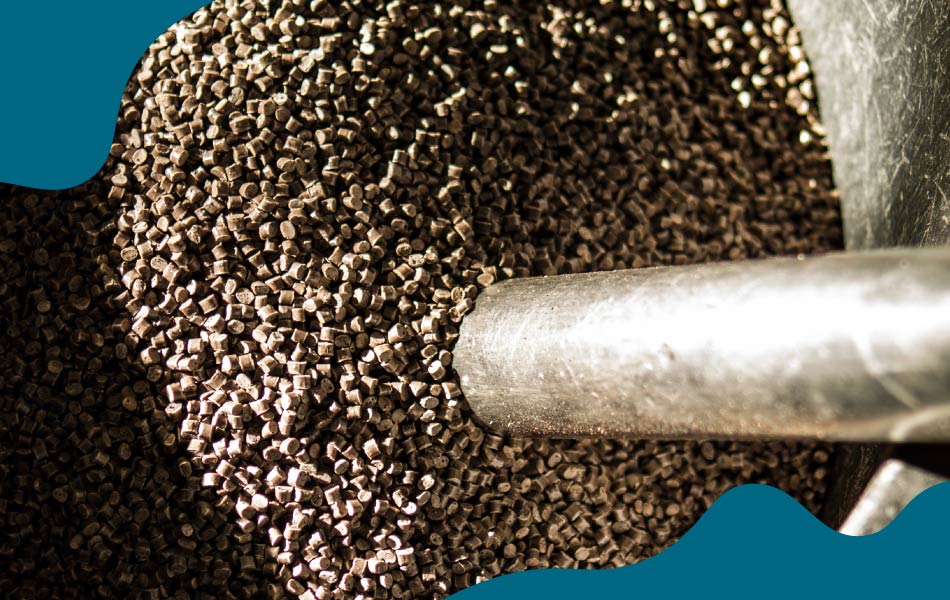
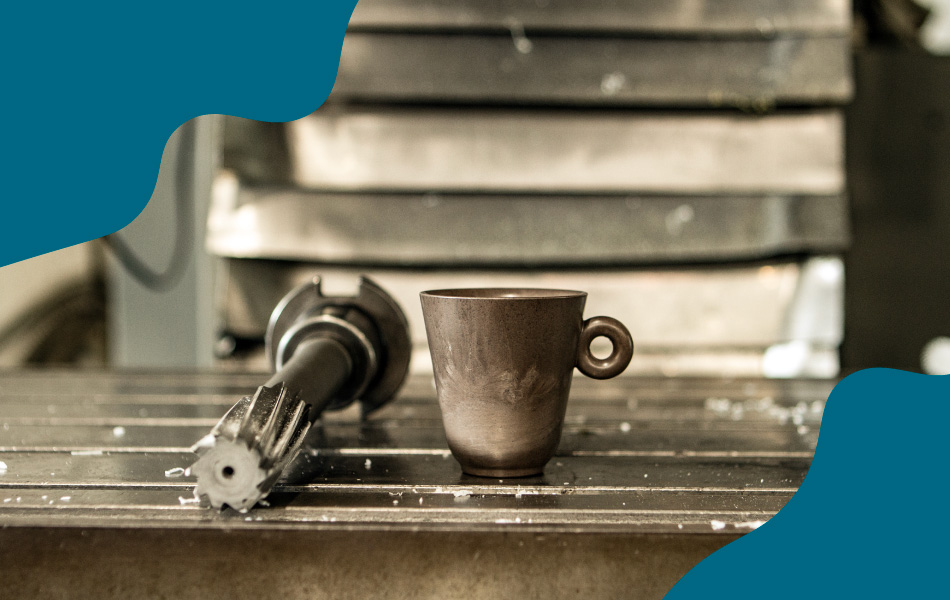
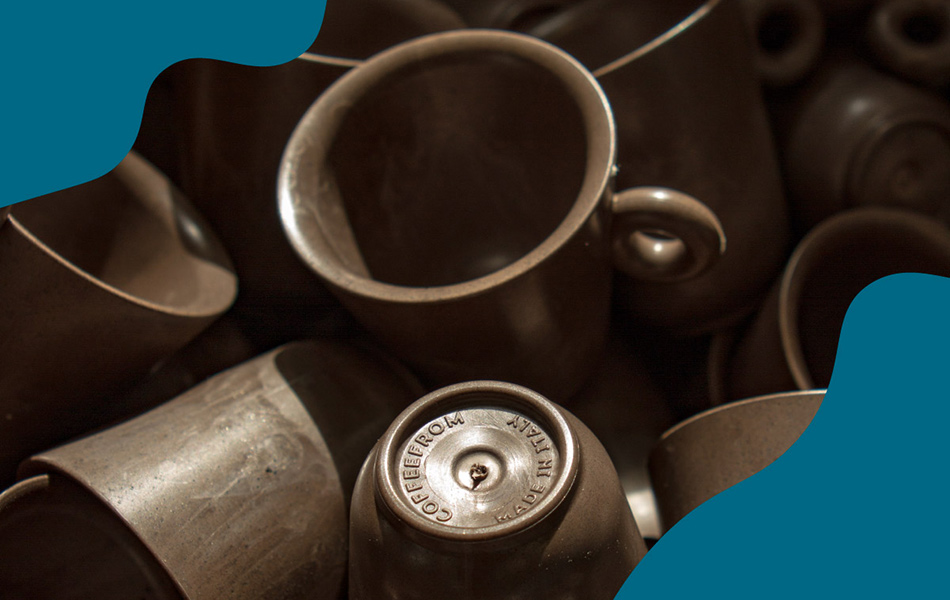
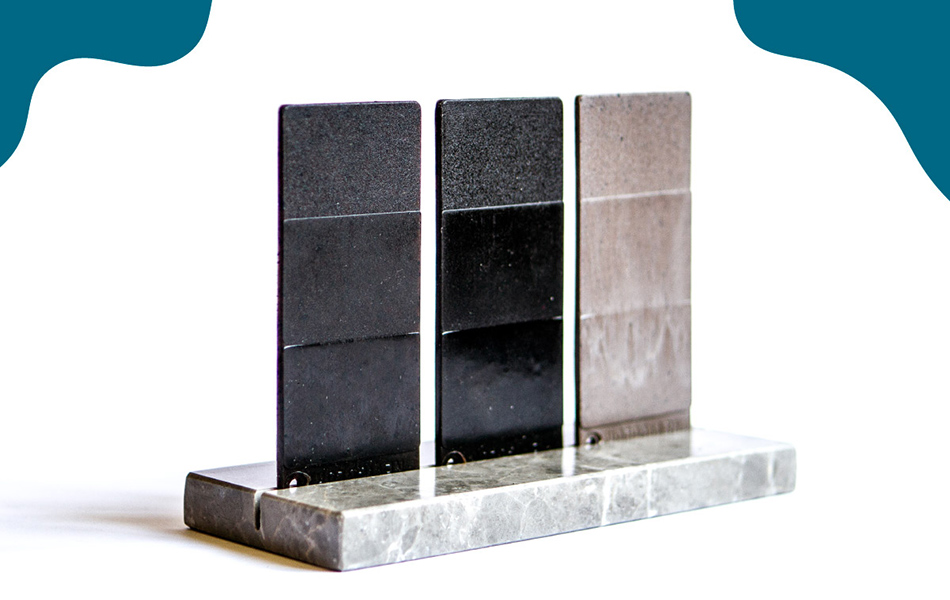
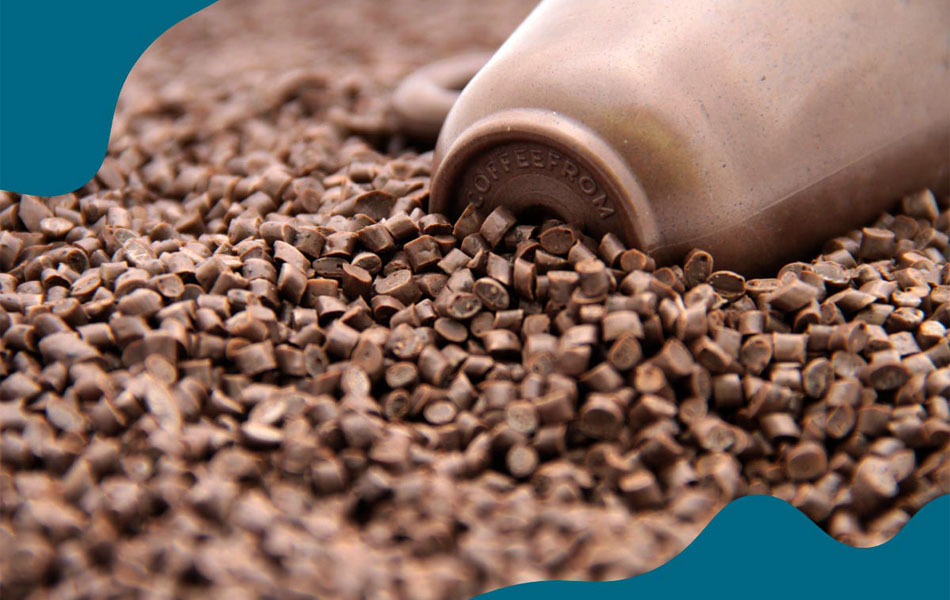
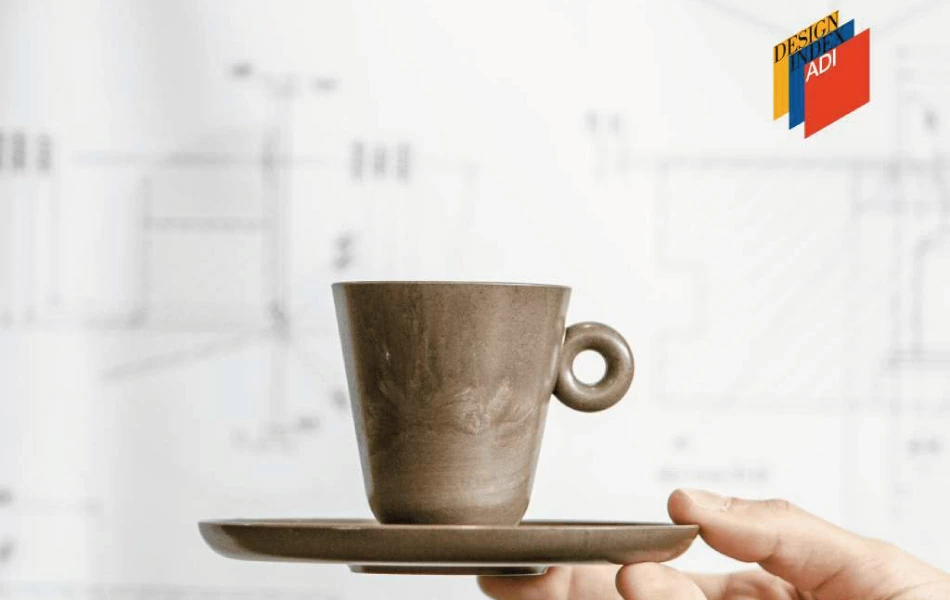
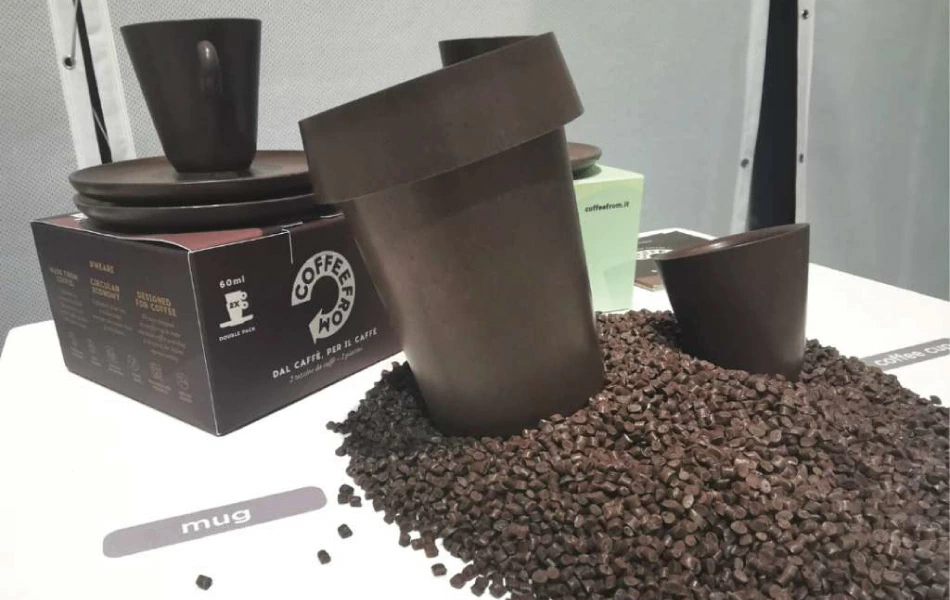
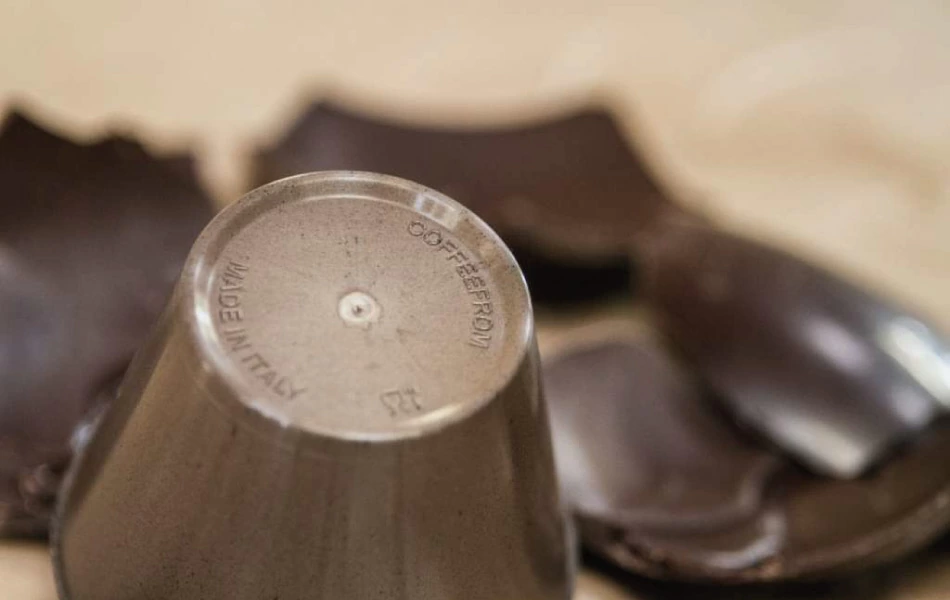
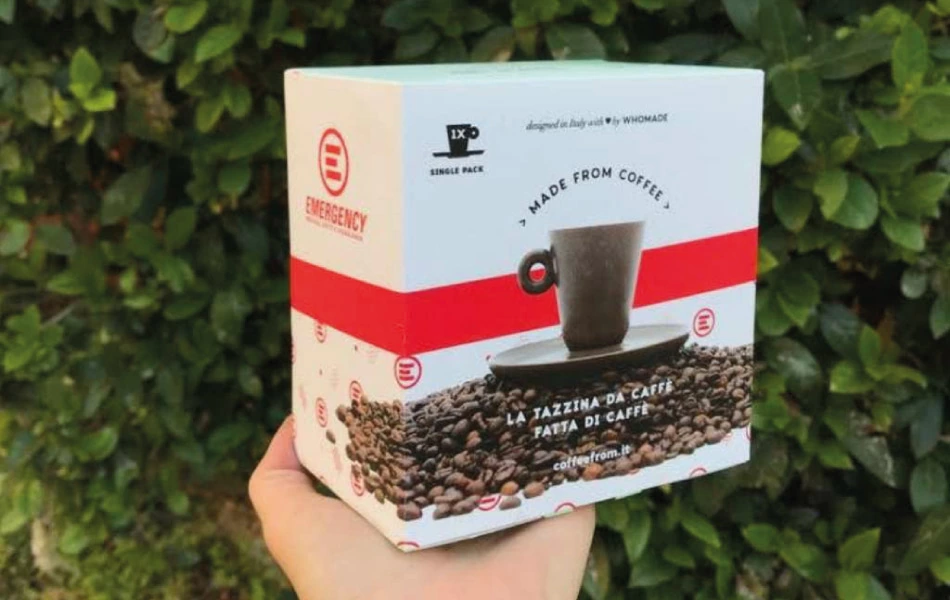
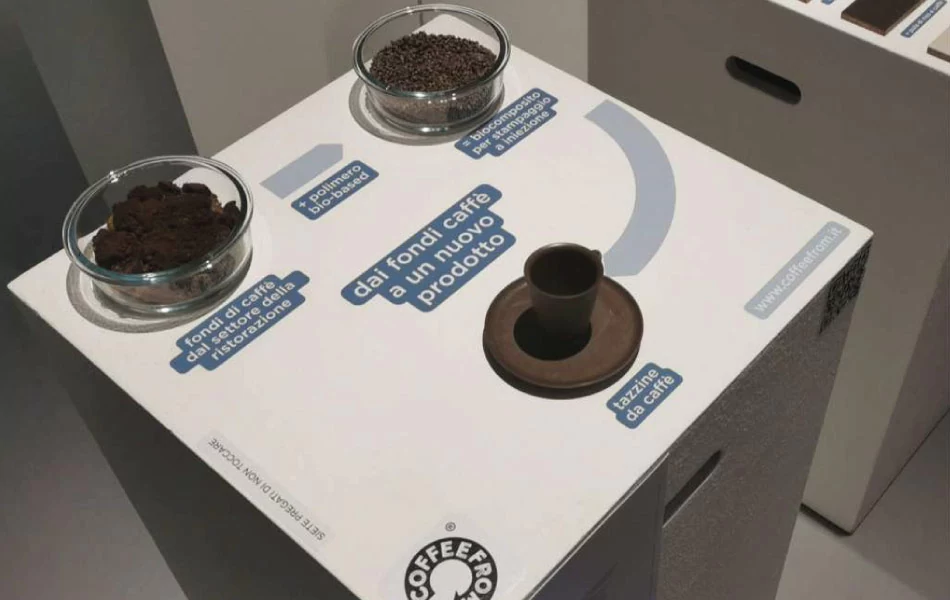
Coffee grounds have found their way into the production of bioplastics and composites. These materials can be used in various industries, from packaging to automotive, offering a biodegradable alternative to conventional plastics. Italian start-up Coffefrom have developed three thermoplastic materials that are partially made of spent coffee grounds. Suitable for injection molding, they can adapt to different applications fields, including packaging, automotive, tableware and service products.
Bioenergy: conversion to biofuels
Spent coffee grounds are rich in organic material, making them suitable for conversion into biofuels. Companies like Bio-Bean in the UK have pioneered the transformation of coffee grounds into biodiesel and bio-pellets, offering a renewable energy source that reduces reliance on fossil fuels.
Agriculture: use as compost and fertilizers
High in nitrogen and other nutrients, spent coffee grounds serve as excellent compost material. They enhance soil quality and promote plant growth, providing a sustainable alternative to chemical fertilizers. Additionally, they are used as a substrate for growing mushrooms, a high-value agricultural product.
Building Materials: inclusion in construction materials
Innovative uses of coffee waste include its incorporation into building materials. For example, Italian restaurant chain Autogrill has developed Wascoffee®, a 100% natural and recyclable material from recycled coffee grounds used to create eco-design furniture in their points of sale.
Food industry: transformation into food-safe products
Spent coffee grounds are being transformed into flour and other food products rich in dietary fiber and antioxidants. Some start-ups are producing gluten-free flour from coffee grounds, which is used in baking and other culinary applications.
Cosmetics: use in health and beauty products
The rich bioactive compounds in spent coffee grounds, such as polyphenols and caffeine, make them valuable for cosmetic applications. They are used in scrubs, masks, and other skincare products for their exfoliating and antioxidant properties.
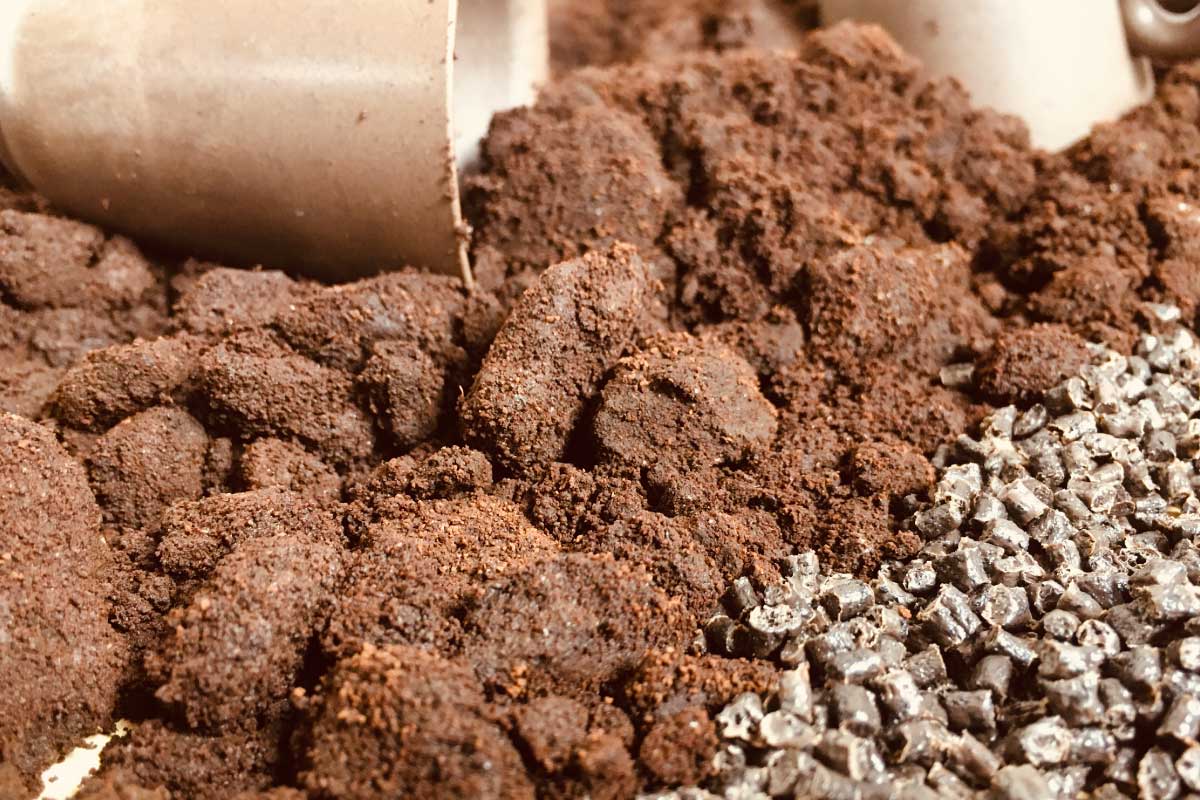

Challenges in scaling Up
Despite the promising applications, scaling up the reuse of spent coffee grounds faces several challenges. Logistical hurdles in the collection and transportation of grounds are significant, as is the need for regulatory frameworks that support the use of coffee byproducts in new applications. Additionally, consumer awareness and acceptance of products derived from coffee waste must be bolstered to create a viable market.
Future potential
The future of spent coffee grounds lies in continued research and innovation. Investment in developing efficient processing technologies and creating market demand for recycled coffee products will be crucial. With the support of initiatives like the Center for Circular Economy in Coffee (C4CEC), there is potential to transform the coffee industry into a model of circular economy practices.
Conclusions
The reuse of spent coffee grounds is a compelling example of how waste can be turned into valuable resources, driving sustainability and economic growth. By embracing the principles of the circular economy, we can reduce environmental impact and create new opportunities across various sectors. As we look to the future, continued innovation and investment in this area will be vital in making the most of this abundant yet underutilized resource.